How do I know if my acne is bacterial or fungal?
Differentiate between bacterial and fungal acne with our comprehensive guide. Uncover insights on 'How do I know if my acne is bacterial or fungal?'.
How do I know if my acne is bacterial or fungal?
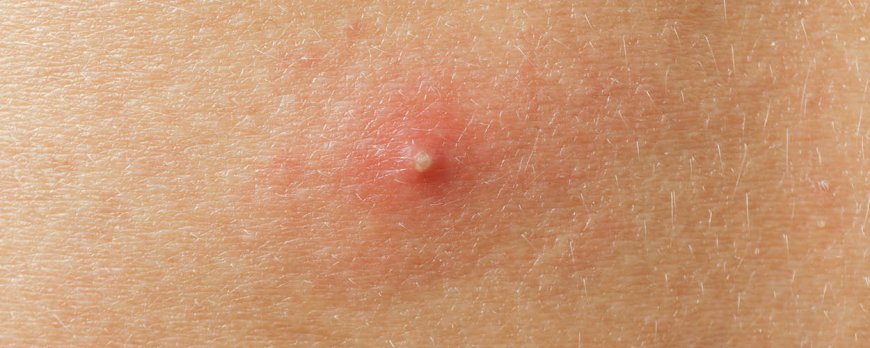
Determining whether your acne is bacterial or fungal requires understanding the different symptoms and signs associated with each type. Bacterial acne is caused by excess sebum clogging hair follicles and is characterized by varying sizes of pimples that can appear on the face, neck, or chest. Fungal acne, on the other hand, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the hair follicles and appears as small, uniform-sized pimples that are often itchy. Fungal acne is commonly found on the arms, chest, and back, while bacterial acne is more common on the face. If you're unsure, it's best to consult a dermatologist who can diagnose the type of acne through a visual examination or by taking a skin scraping or biopsy. Treatment options for bacterial acne may include over-the-counter acne treatments, a healthy diet, and good skincare practices, while fungal acne is typically treated with antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications. Preventive measures for fungal acne include showering after sweating, wearing breathable fabrics, and using dandruff shampoo regularly.
Key Takeaways:
- Determining if your acne is bacterial or fungal is crucial for effective treatment.
- Bacterial acne is caused by excess sebum and appears as varying sizes of pimples on the face, neck, or chest.
- Fungal acne is characterized by small, uniform-sized pimples that are itchy and commonly found on the arms, chest, and back.
- Consulting a dermatologist is recommended to accurately diagnose the type of acne.
- Treatment options for bacterial acne include over-the-counter treatments, a healthy diet, and good skincare habits.
What is bacterial acne?
Bacterial acne occurs due to excess sebum clogging the hair follicles and is characterized by specific symptoms and signs. This type of acne is caused by an overproduction of sebum, which is an oily substance that helps lubricate the skin. When there is an excessive amount of sebum, it can mix with dead skin cells and bacteria, leading to the clogging of hair follicles.
One of the primary signs of bacterial acne is the presence of pimples that come in varying sizes. These pimples can range from small, red bumps to large, swollen nodules. Bacterial acne is most commonly found on the face, but it can also appear on the neck, chest, and back.
Other symptoms of bacterial acne may include blackheads, whiteheads, and pustules. Blackheads are small, dark bumps that form when a hair follicle becomes clogged with sebum and dead skin cells. Whiteheads are similar to blackheads but are covered by a thin layer of skin. Pustules are inflamed, pus-filled bumps that are often painful and tender to the touch.
If you suspect that you have bacterial acne, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis. A dermatologist will be able to visually examine your skin and may also take a skin scraping or perform a biopsy to determine the type of acne you have. They can then recommend appropriate treatment options based on the severity of your condition.
What is fungal acne?
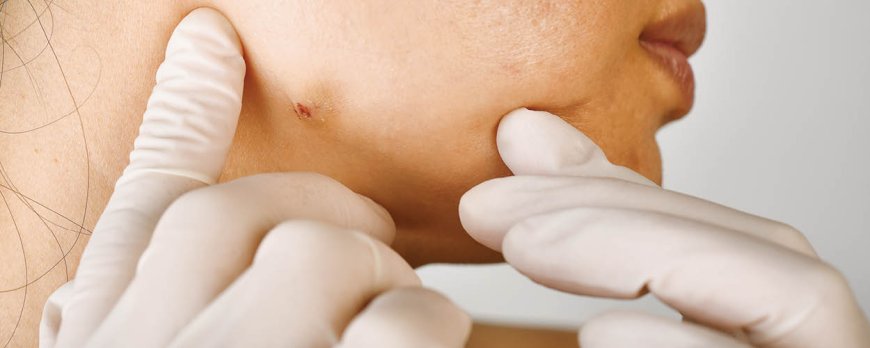
Fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the hair follicles and exhibits distinct symptoms and signs. Unlike bacterial acne, fungal acne appears as small, uniform-sized pimples that are often itchy. These tiny bumps can be found on the arms, chest, and back, and tend to multiply in clusters. Fungal acne is most commonly seen in individuals with oily skin or those who sweat excessively, as the yeast thrives in warm, moist environments.
Recognizing the symptoms of fungal acne is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. One of the key indicators is the appearance of pustules that resemble small whiteheads. These pimples may also have a reddish or yellowish hue. It's important to note that unlike bacterial acne, fungal acne does not typically present with blackheads or larger cystic lesions.
If you suspect that you have fungal acne, it's essential to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. A visual examination by a medical professional can help confirm the presence of fungal acne. In some cases, the dermatologist may also opt to take a skin scraping or biopsy to rule out other conditions and ensure an appropriate treatment plan is followed.
Common signs of fungal acne:
- Small, uniform-sized pimples
- Clusters of pustules
- Pimples that are itchy
- Lack of blackheads or larger cysts
Understanding the differences between bacterial and fungal acne is important for effective treatment. With the guidance of a dermatologist, appropriate treatment options for fungal acne may include antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications. To prevent future outbreaks, it is recommended to practice good hygiene by showering after sweating, wearing breathable fabrics, and regularly using dandruff shampoo.
Distinguishing between bacterial and fungal acne
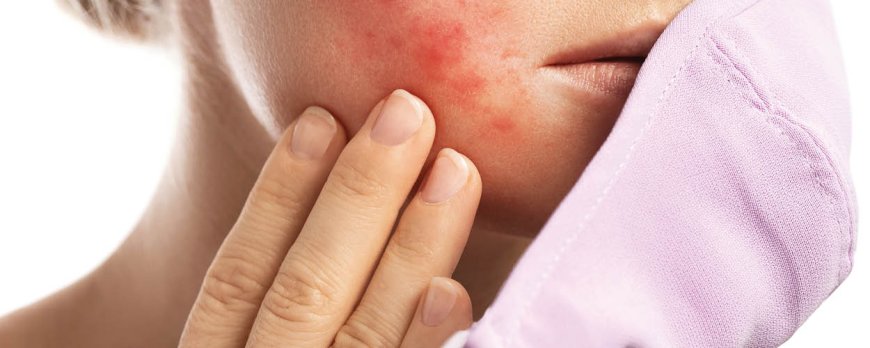
Distinguishing between bacterial and fungal acne can be done by observing the differences in symptoms and locations. Bacterial acne is characterized by varying sizes of pimples that can appear on the face, neck, or chest. These pimples may be red or inflamed, and they may contain pus. On the other hand, fungal acne appears as small, uniform-sized pimples that are often itchy. These pimples are typically found on the arms, chest, and back. They may be accompanied by redness and a rash-like appearance.
Symptoms of bacterial acne:
- Varying sizes of pimples
- Redness and inflammation
- Pus-filled pimples
- Commonly found on the face, neck, or chest
Symptoms of fungal acne:
- Small, uniform-sized pimples
- Itchiness
- Redness and rash-like appearance
- Commonly found on the arms, chest, and back
If you're unsure about the type of acne you have, it's best to consult a dermatologist. A dermatologist can provide a proper diagnosis by conducting a visual examination of your skin or by taking a skin scraping or biopsy. This will help determine whether your acne is bacterial or fungal and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment options for bacterial acne may include over-the-counter acne treatments, maintaining a healthy diet, and practicing good skincare habits. On the other hand, fungal acne is typically treated with antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications. It's important to follow the recommended treatment plan prescribed by your dermatologist to effectively manage and treat your acne.
In addition to treatment, preventive measures can also help minimize the occurrence of fungal acne. These measures include showering after sweating, wearing breathable fabrics, and regularly using dandruff shampoo. By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can help prevent the recurrence of fungal acne and maintain healthier skin.
The Importance of Consulting a Dermatologist
Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for a proper diagnosis of whether your acne is bacterial or fungal. Dermatologists are highly trained professionals who specialize in skin conditions and can accurately identify the type of acne you are experiencing. They can conduct a visual examination of your skin and may even take a skin scraping or biopsy to further confirm the diagnosis.
Determining the type of acne is essential because bacterial and fungal acne require different treatment approaches. Bacterial acne is commonly treated with over-the-counter acne treatments, maintaining a healthy diet, and adopting good skincare practices. On the other hand, fungal acne is typically managed with antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications.
In addition to diagnosing and treating acne, dermatologists can provide personalized advice on preventive measures. They can recommend proper skincare routines, including suitable cleansers and moisturizers, to manage both bacterial and fungal acne. They can also provide guidance on lifestyle changes, such as showering after sweating and wearing breathable fabrics, to prevent the occurrence of fungal acne.
Benefits of Consulting a Dermatologist:
- Accurate diagnosis of the type of acne
- Access to specialized knowledge and expertise
- Possible skin scraping or biopsy for precise diagnosis
- Customized treatment plans based on individual needs
- Preventive measures and guidance for long-term acne management
Remember, acne can have various causes, and self-diagnosing can be challenging. By consulting a dermatologist, you can ensure that you receive the most effective treatment for your specific type of acne and prevent future breakouts.

Treatment options for bacterial acne
Treating bacterial acne involves a combination of over-the-counter treatments, a healthy diet, and proper skincare practices. Here are some options to consider:
- Over-the-counter acne treatments: There are numerous products available that contain ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, which can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin. These treatments come in various forms such as cleansers, creams, gels, and spot treatments.
- Healthy diet: While diet alone may not directly cause or cure acne, maintaining a balanced diet can contribute to overall skin health. Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help support skin health and reduce inflammation.
- Skincare practices: Establishing a regular skincare routine is crucial for managing bacterial acne. Cleanse your face twice a day using a gentle cleanser suitable for acne-prone skin. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as it can irritate the skin and worsen acne. Follow up with a non-comedogenic moisturizer to hydrate the skin without clogging pores. It's also essential to avoid picking or popping acne, as this can lead to scarring and further infection.
When to seek professional help
If over-the-counter treatments do not effectively manage your bacterial acne or if your acne is severe, it's advisable to consult a dermatologist. They can provide a more personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs. A dermatologist may recommend prescription medications, such as antibiotics or topical retinoids, to target bacteria and promote skin cell turnover. They can also offer guidance on lifestyle changes and additional skincare practices to improve your acne management.
Remember, everyone's skin is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It may take some trial and error to find the most effective treatment for your bacterial acne. Stay consistent with your skincare routine, be patient, and don't hesitate to seek professional help if needed.
Treatment options for fungal acne
Fungal acne is typically treated using antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications. These treatment options help to eliminate the overgrowth of yeast in the hair follicles and alleviate the symptoms of fungal acne.
Antifungal creams
Topical antifungal creams are often recommended for treating fungal acne. These creams contain active ingredients that target and eliminate the overgrowth of yeast on the skin. They are typically applied directly to the affected areas, following the instructions provided by your dermatologist or the product packaging. It's important to use the cream regularly and as directed to achieve the best results.
Antifungal shampoos
In some cases, fungal acne may also appear on the scalp, causing itchiness and discomfort. Antifungal shampoos can be used to effectively treat fungal acne on the scalp. These shampoos contain antifungal ingredients that help to control the yeast overgrowth and reduce symptoms. It is recommended to lather the shampoo into the scalp and leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing thoroughly. Regular use, as prescribed by your dermatologist, can help alleviate the symptoms of fungal acne on the scalp.
Oral medications
In more severe cases of fungal acne, oral medications may be prescribed by a dermatologist. These medications are taken internally and work to eliminate the overgrowth of yeast from within the body. Oral medications for fungal acne should be taken exactly as prescribed and for the full duration of the treatment course. It's important to follow your dermatologist's instructions and inform them of any possible side effects or concerns during the course of treatment.
Remember, it's always best to consult with a dermatologist before starting any treatment for fungal acne. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment options based on your specific condition and needs. With proper treatment and care, fungal acne can be effectively managed and relieved.
Preventive Measures for Fungal Acne
Taking certain preventive measures can help reduce the risk of fungal acne and its recurrence. By incorporating these habits into your routine, you can maintain healthier skin and minimize the chances of fungal acne flare-ups.
- Showering after sweating: After engaging in physical activities that result in sweating, it is essential to shower and cleanse your skin thoroughly. Sweat can create a moist environment that encourages the growth of fungi, so rinsing off sweat promptly can help prevent fungal acne from developing.
- Wearing breathable fabrics: Clothing made from natural, breathable materials such as cotton or linen can help prevent fungal acne. These fabrics allow air to circulate and reduce the likelihood of sweat being trapped against the skin, which can contribute to fungal growth.
- Using dandruff shampoo: If you notice signs of fungal acne on your scalp or other areas prone to dandruff, using a dandruff shampoo containing antifungal ingredients can be beneficial. These shampoos help control the yeast overgrowth that can lead to fungal acne breakouts.
- Maintaining good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene is crucial in preventing the development and spread of fungal acne. Regularly wash your face, body, and hair with gentle cleansers to remove excess oil, sweat, and dead skin cells that can create an environment conducive to fungal growth.
By following these preventive measures, you can help keep fungal acne at bay and promote healthier skin. However, it's important to note that if you suspect you have fungal acne or experience persistent acne issues, it is always best to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.

Conclusion
By understanding the symptoms, signs, and treatment options, you can determine whether your acne is bacterial or fungal and take appropriate steps to manage it. Bacterial acne is caused by excess sebum clogging hair follicles and is characterized by varying sizes of pimples that can appear on the face, neck, or chest. On the other hand, fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the hair follicles and appears as small, uniform-sized pimples that are often itchy. Fungal acne is commonly found on the arms, chest, and back, while bacterial acne is more common on the face.
If you're unsure about the type of acne you have, it's best to consult a dermatologist who can diagnose it through a visual examination or by taking a skin scraping or biopsy. Dermatologists are experts in diagnosing and treating various skin conditions, including acne. They can provide valuable insights and recommend the most appropriate treatment based on your specific situation.
Treatment options for bacterial acne may include over-the-counter acne treatments, maintaining a healthy diet, and practicing good skincare habits. On the other hand, fungal acne is typically treated with antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications. It's important to follow the treatment plan recommended by your dermatologist to effectively manage your acne and prevent further breakouts.
Additionally, taking preventive measures can help minimize the occurrence of fungal acne. These measures include showering after sweating, wearing breathable fabrics, and regularly using dandruff shampoo. By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can reduce the chances of developing fungal acne and maintain healthy skin.
FAQ
How do I know if my acne is bacterial or fungal?
To determine if your acne is bacterial or fungal, it's important to understand the symptoms and signs of each condition. Bacterial acne is caused by excess sebum clogging hair follicles and is characterized by varying sizes of pimples that can appear on the face, neck, or chest. Fungal acne, on the other hand, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the hair follicles and appears as small, uniform-sized pimples that are often itchy. Fungal acne is commonly found on the arms, chest, and back, while bacterial acne is more common on the face. If you're unsure, it's best to consult a dermatologist who can diagnose the type of acne through a visual examination or by taking a skin scraping or biopsy.
What is bacterial acne?
Bacterial acne is caused by excess sebum clogging hair follicles. It is characterized by varying sizes of pimples that can appear on the face, neck, or chest. The primary cause of bacterial acne is the overproduction of sebum, which leads to clogged hair follicles. Signs of bacterial acne include pimples that can range in size and may be accompanied by inflammation. Treatment options for bacterial acne may include over-the-counter acne treatments, a healthy diet, and good skincare practices.
What is fungal acne?
Fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the hair follicles. It appears as small, uniform-sized pimples that are often itchy. Fungal acne is commonly found on the arms, chest, and back. Unlike bacterial acne, which can vary in size, fungal acne tends to have consistent and uniform-sized pimples. Treatment options for fungal acne typically involve the use of antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications. Preventive measures for fungal acne include showering after sweating, wearing breathable fabrics, and using dandruff shampoo regularly.
How can I differentiate between bacterial and fungal acne?
Bacterial and fungal acne can be differentiated based on their symptoms. Bacterial acne is characterized by varying sizes of pimples that can appear on the face, neck, or chest, whereas fungal acne appears as small, uniform-sized pimples that are often itchy and commonly found on the arms, chest, and back. The location and size of the pimples can help in determining whether the acne is bacterial or fungal.
Why is it important to consult a dermatologist?
Consulting a dermatologist is important to accurately diagnose the type of acne. A dermatologist can conduct a visual examination, skin scraping, or biopsy to identify whether the acne is bacterial or fungal. This is important as the treatment options for bacterial and fungal acne differ, and a proper diagnosis ensures that the appropriate treatment is administered.
What are the treatment options for bacterial acne?
Treatment options for bacterial acne may include over-the-counter acne treatments, adopting a healthy diet, and practicing good skincare habits. Over-the-counter acne treatments can help manage bacterial acne by reducing inflammation and unclogging pores. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can also contribute to healthier skin. Additionally, maintaining good skincare practices, such as gentle cleansing and avoiding excessive oil-based products, can help manage bacterial acne.
What are the treatment options for fungal acne?
Treatment options for fungal acne typically involve the use of antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications. Antifungal creams can be applied topically to affected areas, while antifungal shampoos can be used on the scalp or body. In more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed by a dermatologist. It is important to follow the instructions provided by a healthcare professional when using these treatments.
How can I prevent fungal acne?
Preventive measures for fungal acne include showering after sweating, wearing breathable fabrics, and regularly using dandruff shampoo. Showering after sweating helps to remove excess moisture and bacteria from the skin. Wearing breathable fabrics allows the skin to breathe and reduces the risk of moisture buildup. Regular use of dandruff shampoo, which contains antifungal properties, can help prevent the overgrowth of yeast on the scalp and body.



































































































































