What does bacterial pimples look like?
Unearth the mystery of bacterial pimples by answering 'What does bacterial pimples look like?'. Dive into their characteristics, causes, and treatments today.

What does bacterial pimples look like?
Bacterial pimples, also known as infected pimples or bacterial acne, have distinct characteristics that set them apart from regular pimples. These pimples are typically caused by a bacterial infection and may require different treatment than regular pimples or acne. They can occur when pores on the skin become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, or bacteria. Infected pimples are more likely to occur when a pimple is popped or when a person has cystic acne. They can be larger, redder, and more painful than regular pimples and may take longer to heal. Infected pimples may be filled with pus and can have other symptoms such as being more obvious, painful, or sensitive to touch. They can also be a result of staph infections, which can cause boils or impetigo. It is important to consult a doctor or dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Key Takeaways:
- Bacterial pimples are caused by a bacterial infection and require different treatment than regular pimples.
- They can be larger, redder, and more painful than regular pimples, taking longer to heal.
- Infected pimples may be filled with pus and exhibit symptoms such as being more obvious, painful, or sensitive.
- They can result from popping pimples, having cystic acne, or staph infections.
- Consulting a doctor or dermatologist is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Characteristics of Bacterial Pimples
Bacterial pimples are typically larger, redder, and more painful than regular pimples. These pesky blemishes can be quite noticeable and may take longer to heal compared to other types of pimples. They are often filled with pus and can feel tender and sensitive to the touch.
One of the key characteristics of bacterial pimples is their association with infections. When a pimple is popped or when a person has cystic acne, there is a higher chance of developing an infected pimple. Infections can also be caused by staph bacteria, leading to the formation of boils or impetigo.
Identifying the signs of bacterial pimples is crucial for appropriate treatment. Infected pimples may have distinct symptoms such as pain, redness, and swelling. They can be more obvious than regular pimples, standing out on the skin's surface. Additionally, they are often more sensitive and can cause discomfort when touched or pressed.
Signs of Bacterial Pimples:
- Larger and redder than regular pimples
- Filled with pus
- Tender and painful to touch
- More obvious on the skin's surface
- Increased sensitivity and discomfort
If you suspect you have bacterial pimples, it is important to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. They can provide guidance on how to effectively address the bacterial infection, which may involve killing the bacteria causing the infection. In more severe cases, antibiotics might be prescribed to combat the infection.
While medical intervention is crucial, there are also home remedies that can assist in alleviating symptoms and promoting healing. Warm compresses can help reduce inflammation, while benzoyl peroxide creams can aid in killing bacteria on the skin's surface. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene by keeping the affected area clean is essential.
Prevention and precautions are essential to minimize the occurrence and spread of bacterial pimples. Avoid scratching or popping pimples as this can lead to further infection and scarring. It is also advisable to refrain from using makeup around the affected area, as this can exacerbate the condition.
If the infection does not improve or symptoms worsen after a couple of weeks, it may be necessary to explore more invasive treatments. In such cases, consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist is crucial to determine the best course of action and prevent potential complications.
Causes of Bacterial Pimples
Bacterial pimples can occur when pores on the skin become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, or bacteria. This can lead to an infection, resulting in the formation of bacterial pimples. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of these pimples:
- Clogged Pores: When excess oil, dirt, and dead skin cells accumulate in the pores, it can create an environment for bacteria to thrive. This can lead to the formation of bacterial pimples.
- Cystic Acne: People with cystic acne are more prone to developing bacterial pimples. Cystic acne is a severe form of acne that causes deep, painful cysts or nodules to form beneath the skin.
- Staph Infections: Bacterial pimples can also occur as a result of staph infections. Staphylococcus bacteria can infect the hair follicles, leading to the formation of boils or impetigo, which are contagious skin infections.
It is important to note that not all pimples are bacterial in nature. Regular pimples or acne can be caused by hormonal changes, excess oil production, or a buildup of dead skin cells. However, if you suspect that you have bacterial pimples, it is recommended to consult a doctor or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment for bacterial pimples typically involves targeting the underlying bacterial infection. This can be done through the use of topical medications or oral antibiotics. In more severe cases, drainage or incision of the pimple may be necessary. Additionally, home remedies such as warm compresses and benzoyl peroxide creams can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
In order to prevent the occurrence of bacterial pimples, it is essential to maintain a good skincare routine. This includes keeping the skin clean, avoiding the use of heavy or pore-clogging cosmetics, and refraining from picking or popping pimples. By taking these precautions and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary, it is possible to manage and prevent bacterial pimples effectively.
Symptoms of Bacterial Pimples
Infected pimples may be filled with pus and exhibit symptoms such as being more obvious, painful, or sensitive to touch. These symptoms can make the infected pimples stand out from regular acne or pimples. The affected area may appear redder and larger than a typical pimple, and it may take longer to heal. The presence of pus indicates a bacterial infection and can contribute to the increased pain and sensitivity.
In addition to the physical symptoms, infected pimples can also be accompanied by other signs. They may feel warm to the touch and may develop a firm, raised bump. Sometimes, the area surrounding the pimple can become swollen or inflamed. It's important to note that infected pimples can also be a result of staph infections, which can cause boils or impetigo.
Common symptoms of bacterial pimples include:
- Obvious visual appearance
- Increased pain or tenderness
- Heightened sensitivity to touch
- Pus-filled lesion
- Inflammation or redness
- Warmth in the affected area
- Swelling or firmness
If you suspect that you have bacterial pimples or notice any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a doctor or dermatologist for diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They can provide a proper evaluation and recommend a suitable course of action to address the infection and promote healing.
Remember, early recognition and prompt treatment of bacterial pimples can help prevent further complications, such as scarring or potential spread of the infection. Take the necessary precautions and seek medical attention when needed to ensure optimal care for your skin.
Diagnosis of Bacterial Pimples
To accurately diagnose bacterial pimples, it is crucial to consult a doctor or dermatologist. They have the expertise to identify the specific causes and characteristics of the infection, ensuring an appropriate treatment plan. Here are some key steps involved in diagnosing bacterial pimples:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will perform a thorough examination of the affected areas, assessing the appearance and characteristics of the pimples. They may also check for any signs of accompanying skin infections, such as boils or impetigo.
- Medical History: The doctor will inquire about your medical history, including any previous instances of acne or skin infections. They may also ask about your skincare routine, lifestyle factors, and any recent changes that could contribute to the development of bacterial pimples.
- Diagnostic Techniques: In some cases, the doctor may need to collect a sample from the pimple for further analysis. This could involve swabbing the affected area to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Specialist Referral: If the doctor suspects any underlying conditions contributing to the bacterial pimples, they may refer you to a dermatologist or other specialists for further evaluation and treatment.
Remember, self-diagnosis is not recommended when it comes to bacterial pimples. Many other skin conditions can mimic the appearance of infected pimples, and only a trained medical professional can provide an accurate diagnosis.
By seeking medical attention promptly, you can ensure that you receive the most appropriate treatment and prevent any potential complications. Early recognition and diagnosis are key in effectively managing bacterial pimples and promoting skin health.
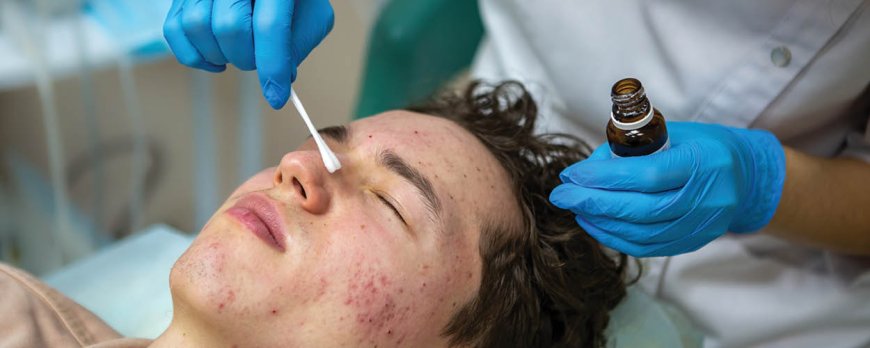
Treatment options for bacterial pimples
Treatment for bacterial pimples involves targeting the bacteria that causes the infection, with antibiotics being prescribed in severe cases. It is important to consult a doctor or dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are some treatment options to consider:
- Topical medications: Over-the-counter or prescription creams and gels containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or sulfur can help kill the bacteria causing the infection and reduce inflammation. These can be applied directly to the affected area.
- Oral antibiotics: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be necessary to combat the bacterial infection. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline. These medications work by killing the bacteria from within the body.
- Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin, also known as Accutane, is a potent oral medication used to treat severe cystic acne. It reduces oil production in the skin, kills bacteria, and helps prevent clogged pores. However, it is associated with several potential side effects and should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
- In-office procedures: In some cases, more invasive treatments may be necessary if bacterial pimples do not respond to other treatments. These can include procedures such as drainage and extraction of pus, laser therapy, or chemical peels. These procedures are typically performed by dermatologists or skincare professionals.
It is important to note that self-treating bacterial pimples with home remedies may not be effective in all cases. While warm compresses and benzoyl peroxide creams can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing, they may not address the underlying bacterial infection. Therefore, it is recommended to seek professional medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Additionally, it is crucial to take preventive measures to minimize the occurrence of bacterial pimples. Avoid popping or scratching pimples, as this can introduce more bacteria into the affected area and potentially worsen the infection. It is also important to maintain a clean and hygienic skincare routine, keeping the affected area clean but avoiding excessive washing, which can strip the skin of its natural oils and aggravate the condition.
If the infection does not improve or if the symptoms worsen after a couple of weeks of treatment, it is important to follow up with a healthcare professional. They may recommend further treatment options or evaluate if there are any underlying conditions contributing to the persistent bacterial pimples.
Home Remedies for Bacterial Pimples
Along with medical treatment, there are several home remedies that can aid in the healing of bacterial pimples. These remedies can help reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and promote faster recovery. Here are some effective home remedies for bacterial pimples:
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help reduce swelling and promote blood circulation. This can aid in the healing process by bringing nutrients and immune cells to the site of the infection. Simply soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring out the excess, and gently press it against the pimple for 10-15 minutes, a few times a day.
- Benzoyl Peroxide Creams: Benzoyl peroxide is known for its antibacterial properties, making it an effective treatment for bacterial pimples. It helps kill the bacteria causing the infection and can also unclog pores. Apply a thin layer of benzoyl peroxide cream to the affected area once or twice a day, following the instructions on the product label.
- Keeping the Area Clean: Maintaining good hygiene is crucial when dealing with bacterial pimples. Wash the affected area gently with a mild cleanser and warm water twice a day. Avoid scrubbing or using harsh chemicals, as this can further irritate the skin. Pat the area dry with a clean towel after washing.
If a pimple becomes painful, swollen, or shows signs of infection, it is essential to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can diagnose the condition accurately and recommend appropriate treatment options. Remember, it is crucial to refrain from scratching or popping pimples, as this can lead to further infection and scarring. Additionally, avoid using makeup or oily products around the affected area, as they can worsen the condition. By combining medical treatment with these home remedies, you can help speed up the healing process and prevent future flare-ups of bacterial pimples.
Precautions and Prevention
Taking precautionary measures can help prevent the occurrence and worsening of bacterial pimples. Here are some important steps to follow:
- Avoid scratching or popping pimples: While it may be tempting to squeeze or pick at a pimple, doing so can spread the infection and lead to more severe inflammation or scarring.
- Avoid using makeup around the affected area: Cosmetics, especially oil-based ones, can clog the pores and exacerbate the bacterial infection. It is best to let the skin breathe and heal.
- Keep the area clean: Regularly wash the affected area with a gentle cleanser to remove any excess oil, dirt, or bacteria that may contribute to the development of bacterial pimples.
- Avoid using greasy or pore-clogging products: Select skincare and haircare products that are labeled as non-comedogenic or oil-free to minimize the risk of clogging the pores and aggravating the condition.
- Wash your hands frequently: Regular hand hygiene can help prevent the spread of bacteria to your face and the development of new pimples.
- Practice good skincare hygiene: Use clean towels, pillowcases, and makeup brushes to minimize the potential for bacterial contamination.
By following these precautions and preventive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of bacterial pimples and help promote healthier skin.
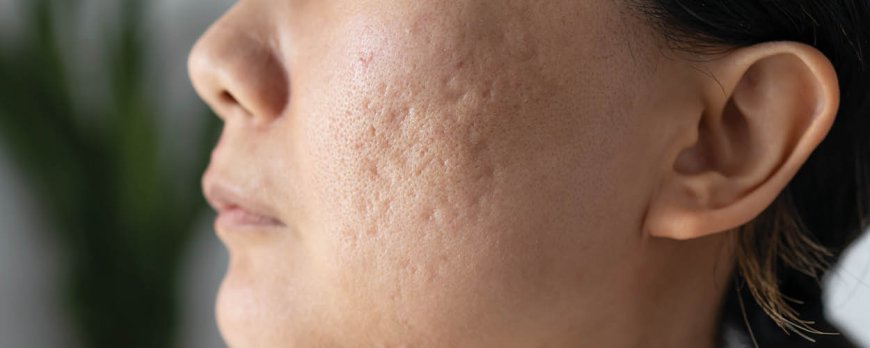
Potential Complications of Bacterial Pimples
If left untreated, bacterial pimples can lead to complications such as scarring and may also be contagious. It is important to be aware of these potential complications and take the necessary steps to prevent them.
1. Scarring: Infected pimples can cause scarring, especially if they are picked, popped, or not properly treated. The inflammation and damage caused by the infection can result in permanent scarring, which can affect the appearance and texture of the skin. To minimize the risk of scarring, it is essential to avoid squeezing or manipulating the infected pimples and to seek appropriate medical treatment.
2. Contagiousness: Bacterial pimples can be contagious, particularly if they are caused by a staph infection. Staph bacteria can easily spread from one person to another through direct contact or by sharing personal items, such as towels or razors. It is crucial to maintain good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and using clean towels and bedding, to prevent the spread of bacterial pimples to others.
If you suspect that you have bacterial pimples or are experiencing any symptoms associated with them, it is vital to consult a doctor or dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help prevent complications, promote healing, and minimize the risk of scarring or contagion. Remember to follow the recommended treatment plan and take necessary precautions to maintain good skin health.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Bacterial Pimples
It is important to seek medical attention if bacterial pimples persist, worsen, or do not improve after a few weeks. While many cases of bacterial pimples can be effectively treated with home remedies and over-the-counter products, there are instances where professional medical intervention is necessary. Here are some situations where seeking medical attention is advised:
- Persistent symptoms: If the infection does not show signs of improvement after a couple of weeks or if the symptoms worsen, it is recommended to consult a doctor or dermatologist. They can evaluate the condition and provide appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
- Severe symptoms: If you experience severe pain, swelling, or redness around the infected pimple, it is crucial to seek medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a more severe infection that requires medical intervention.
- Spread of infection: If the infection spreads to other areas of your face or body or if you notice the development of boils or impetigo, it is important to see a healthcare professional for examination and proper diagnosis. They can determine if further treatment, such as oral antibiotics, is necessary to eradicate the infection.
- Recurring infections: If you have a history of recurring bacterial pimples or if they persist despite your best efforts to treat them, it is advisable to consult a medical professional. They can help identify potential underlying causes and provide targeted treatment options to prevent future infections.
Remember, the earlier you seek medical attention for bacterial pimples, the better chance you have of effectively treating the infection and minimizing the risk of complications, such as scarring. Your healthcare provider can provide valuable guidance and recommend the appropriate course of action to ensure optimal skin health.
Further Treatment Options for Bacterial Pimples
In some cases, more invasive treatments may be required if bacterial pimples do not improve with initial treatments. These additional options aim to address persistent or severe infections that do not respond to standard remedies. The choice of further treatment will depend on the individual's specific condition and the recommendations of a healthcare professional or dermatologist.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses targeted beams of light to kill bacteria and reduce inflammation associated with bacterial pimples. The laser can penetrate deep into the layers of the skin, effectively destroying the bacteria causing the infection. This treatment option can help promote healing and prevent future outbreaks. It is typically performed in a dermatologist's office and may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the outer layer and promotes the growth of new, healthy skin. This treatment can help reduce acne scarring, unclog pores, and eliminate bacteria that lead to infected pimples. Chemical peels can vary in intensity, with mild peels offering a gentler approach and deep peels providing more significant results. A dermatologist can determine the most appropriate type of chemical peel based on the individual's skin condition.
Surgical Drainage
In cases where a bacterial pimple forms an abscess or cyst, surgical drainage may be necessary. This procedure involves making a small incision in the pimple to release the accumulated pus and fluid. By draining the abscess, the pressure is relieved, and the infection can heal more effectively. Surgical drainage should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional to prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms of bacterial pimples despite initial treatments, it is crucial to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can evaluate your condition and recommend the most suitable further treatment options based on your individual needs. Remember, early intervention and appropriate treatment can help prevent complications and promote the healing of bacterial pimples.

Conclusion
Understanding the characteristics and proper treatment of bacterial pimples is essential in managing this particular form of acne. Bacterial pimples, caused by a bacterial infection, require different treatment than regular pimples or acne. They typically occur when pores on the skin become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, or bacteria.
Infected pimples, which can result from popping a pimple or having cystic acne, are larger, redder, and more painful than regular pimples. They may take longer to heal and can be filled with pus. Other symptoms of bacterial pimples include increased visibility, sensitivity to touch, and the possibility of being a result of staph infections, which can cause boils or impetigo.
When dealing with bacterial pimples, it is crucial to consult a doctor or dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Treatment options may involve killing the bacteria causing the infection, and in severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed. Home remedies such as using warm compresses, benzoyl peroxide creams, and keeping the affected area clean can also help alleviate symptoms.
Precautions should be taken to avoid scratching or popping pimples and to refrain from using makeup around the affected area. It is important to note that bacterial pimples can potentially cause scarring and may be contagious. If the infection does not improve or symptoms worsen after a few weeks, more invasive treatments may be necessary to address the issue effectively.
FAQ
What does bacterial pimples look like?
Bacterial pimples can appear larger, redder, and more painful than regular pimples. They may be filled with pus and can have other symptoms such as being more obvious, painful, or sensitive to touch.
What are the characteristics of bacterial pimples?
Bacterial pimples are typically larger, redder, and more painful than regular pimples. They may contain pus, and the area around the pimple may be more obvious, painful, or sensitive.
What causes bacterial pimples?
Bacterial pimples can be caused by a bacterial infection that occurs when pores on the skin become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, or bacteria. They can also be a result of cystic acne or staph infections.
What are the symptoms of bacterial pimples?
Symptoms of bacterial pimples can include the pimple being larger, redder, and more painful than regular pimples. They may contain pus and can be more obvious, painful, or sensitive to touch.
How are bacterial pimples diagnosed?
Bacterial pimples can be recognized and diagnosed by a doctor or dermatologist. It is important to seek professional medical advice for an accurate diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for bacterial pimples?
Treatment options for bacterial pimples can involve killing the bacteria that causes the infection. In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed. It is important to consult a doctor or dermatologist for appropriate treatment.
Are there any home remedies for bacterial pimples?
Home remedies for bacterial pimples can include using warm compresses, benzoyl peroxide creams, and keeping the area clean. However, it is important to consult a medical professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
What precautions should be taken for bacterial pimples?
Precautions for bacterial pimples include avoiding scratching or popping pimples and refraining from using makeup around the affected area. Keeping the area clean and following a skincare routine can also help prevent bacterial pimples.
What are the potential complications of bacterial pimples?
Potential complications of bacterial pimples can include scarring and the possibility of contagion. It is important to seek appropriate treatment to minimize these risks.
When should I seek medical attention for bacterial pimples?
If the infection does not improve or if the symptoms worsen after a couple of weeks, it is important to seek medical attention. A doctor or dermatologist can provide further evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment.
What are the further treatment options for bacterial pimples?
If bacterial pimples do not respond to initial treatments, more invasive procedures may be necessary. It is important to consult a medical professional for guidance on further treatment options.






























































































































