Is my acne hormonal or fungal?
Uncover the cause of your breakouts: 'Is my acne hormonal or fungal?' Understand the differences and find effective treatments for both conditions.
Is my acne hormonal or fungal?
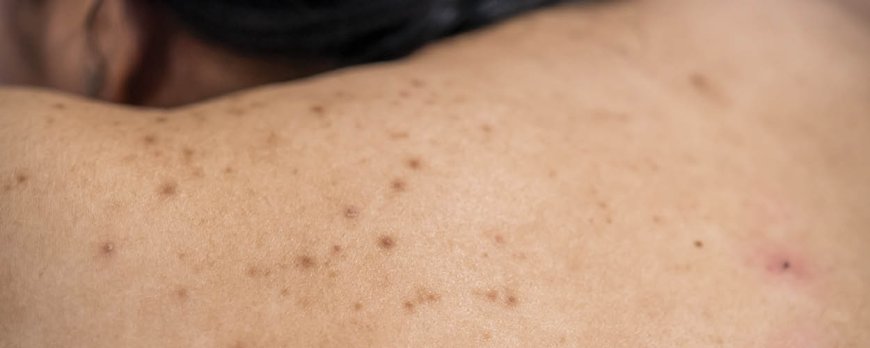
Determining the cause of your acne can be challenging, but understanding whether it is hormonal or fungal is essential for effective treatment. Hormonal acne is caused by changes in hormone levels and appears as deep red and tender cysts, usually in the lower parts of the face. On the other hand, fungal acne is caused by yeast overgrowth in hair follicles and manifests as small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and spread over larger areas. To accurately diagnose your acne, it is best to consult a dermatologist who can examine your skin and consider your medical history.
Key Takeaways:
- Hormonal acne is caused by changes in hormone levels, while fungal acne is caused by yeast overgrowth in hair follicles.
- Hormonal acne appears as deep red and tender cysts, usually in the lower parts of the face, while fungal acne presents as small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and spread over larger areas.
- Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis of acne and to determine whether it is hormonal or fungal.
- Treatment options differ for hormonal and fungal acne, with hormonal acne commonly treated with topical skincare treatments and birth control pills, and fungal acne requiring topical or oral antifungal medication.
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, using non-comedogenic products, and considering lifestyle factors like stress management and diet can help manage both hormonal and fungal acne.
Understanding Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne is primarily caused by changes in hormone levels, leading to the development of deep, red, and tender cysts, often found on the lower parts of the face. These hormonal fluctuations can stimulate the oil glands in the skin, resulting in increased sebum production. The excess oil, along with dead skin cells, can clog the pores, leading to the formation of acne lesions.
While hormonal acne can affect people of all genders and ages, it is most commonly observed in teenagers and women during their menstrual cycle or menopause. Symptoms of hormonal acne may include painful, inflamed cysts that take longer to heal compared to other types of acne.
To effectively manage hormonal acne, various treatment options are available. Topical skincare treatments containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can help reduce inflammation and control excessive oil production. For women, birth control pills can also be prescribed to regulate hormone levels and minimize acne breakouts.
Key Points:
- Hormonal acne is caused by changes in hormone levels and appears as deep, red, and tender cysts.
- Commonly found on the lower parts of the face, hormonal acne can be more difficult to treat due to its severity.
- Treatment options include topical skincare treatments and hormonal therapies like birth control pills.
Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of hormonal acne is crucial for effective management. By consulting a dermatologist, individuals can receive personalized guidance and treatment options to address their specific condition.
Recognizing Fungal Acne
Fungal acne occurs due to yeast overgrowth in hair follicles, resulting in the formation of small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and tend to spread over larger areas of the skin. While it may resemble traditional acne, there are some distinguishing factors to consider when recognizing and diagnosing fungal acne.
Symptoms of Fungal Acne:
- Small, itchy bumps that are often uniform in size
- Clusters of bumps that tend to spread over larger areas, such as the chest, back, and shoulders
- Bumps that may have a white or yellowish appearance
- Itching and discomfort that intensify with sweat or heat
Distinguishing Fungal Acne from Traditional Acne:
Unlike hormonal acne, which typically presents as deep cysts in the lower parts of the face, fungal acne tends to be more widespread and uniform in appearance. It is less likely to cause redness or inflammation and is often accompanied by itching or discomfort. Fungal acne can occur in individuals of all ages and skin types, but it is more prevalent in people who have excessive sweating, wear tight clothing, or use heavy occlusive products.
In order to accurately diagnose fungal acne and determine appropriate treatment, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist. A dermatologist is able to assess the symptoms, conduct a skin examination, and take into account the individual's medical history to provide an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan for fungal acne.
To accurately diagnose whether your acne is hormonal or fungal, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist who can thoroughly examine your skin and consider your medical history.
Finding the underlying cause of acne can be challenging, as hormonal and fungal acne can often have similar symptoms. Hormonal acne is typically caused by changes in hormone levels and is characterized by deep red and tender cysts that commonly appear in the lower parts of the face. On the other hand, fungal acne is caused by yeast overgrowth in hair follicles and presents as small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and spread over larger areas.
A dermatologist will perform a comprehensive skin examination to determine the type of acne you have. They will carefully examine your skin, looking for specific characteristics that can indicate the underlying cause. Additionally, they will take your medical history into consideration, as certain factors such as hormonal imbalances or recent antibiotic use may contribute to acne development.

Diagnosing the Type of Acne
Key Points:
Treating Hormonal Acne
Managing hormonal acne often involves a combination of topical skincare treatments and, in some cases, the use of birth control pills to regulate hormone levels. These treatment options can help reduce inflammation, control excess oil production, and prevent further breakouts.
Topical skincare treatments for hormonal acne typically include ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids. These products work by unclogging pores, reducing bacteria, and promoting cell turnover to prevent acne formation. Regular use of these treatments can help clear existing acne and prevent new breakouts.
In addition to topical treatments, birth control pills can be an effective option for managing hormonal acne in women. Certain birth control pills contain hormones that can regulate and stabilize hormone levels, reducing the occurrence of acne. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable birth control pill based on individual needs and medical history.
It's worth noting that hormonal acne may take time to improve, and it's essential to be patient and consistent with treatment. It's also beneficial to maintain a healthy skincare routine, using non-comedogenic products that do not clog pores. Additionally, managing stress levels, adopting stress-reducing techniques, and following a balanced diet can contribute to overall skin health and acne management.
Treating Fungal Acne
Fungal acne typically requires treatment with specialized antifungal medications, either in topical or oral form, to effectively target the yeast overgrowth responsible for this type of acne. Topical antifungal medications, such as creams or lotions containing ingredients like ketoconazole or ciclopirox, can be applied directly to the affected areas. These medications work by inhibiting the growth of the yeast and reducing inflammation. It is important to follow the instructions provided by your dermatologist or healthcare professional regarding the frequency and duration of application.
In some cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed when topical treatments alone are not sufficient. Oral medications, such as itraconazole or fluconazole, can help eliminate the yeast overgrowth from within the body. This approach is often recommended for more severe or persistent cases of fungal acne. It is essential to take the prescribed oral medication as directed and complete the full course of treatment to ensure effective eradication of the fungal infection.
In addition to antifungal medications, maintaining a consistent skincare routine plays a crucial role in managing fungal acne. Using gentle cleansers and non-comedogenic products can help prevent further irritation and clogged pores. It is important to avoid oily or heavy products that can exacerbate acne symptoms. Implementing good hygiene practices, such as regularly washing pillowcases and avoiding tight-fitting clothing, can also help reduce the risk of fungal acne flare-ups.
Addressing lifestyle factors that may contribute to the overgrowth of yeast, such as minimizing stress levels and adopting a healthy diet, can further support the management of fungal acne. Stress management techniques, such as exercise, meditation, or engaging in hobbies, can help reduce stress-related hormonal fluctuations that may trigger acne. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support overall skin health. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations tailored to your needs.
Summary:
- Fungal acne typically requires treatment with antifungal medications, either in topical or oral form, to target the underlying yeast overgrowth.
- Topical antifungal medications, like creams or lotions, can be directly applied to the affected areas to inhibit yeast growth and reduce inflammation.
- Oral antifungal medications may be prescribed for more severe or persistent cases of fungal acne.
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansers and non-comedogenic products is essential to manage fungal acne.
- Minimizing stress levels, adopting a healthy diet, and practicing good hygiene can also support the management of fungal acne.

Skincare Routine and Lifestyle Factors
In addition to medical treatments, establishing a consistent skincare routine, using non-comedogenic products, managing stress levels, and considering dietary factors can all contribute to better management of both hormonal and fungal acne.
Creating a skincare routine tailored to your skin type and acne condition is essential. Start by cleansing your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and impurities. Follow up with a non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated without clogging pores. Incorporating an exfoliating treatment once or twice a week can help remove dead skin cells and unclog pores, reducing the chances of acne formation.
When selecting products, opt for non-comedogenic options that are specifically formulated to not block pores. Look for ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, which can target and reduce acne-causing bacteria. Additionally, using oil-free or water-based makeup and avoiding heavy, pore-clogging products can help prevent further breakouts.
Managing stress levels is also crucial for maintaining clear skin. Stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, leading to increased acne flare-ups. Incorporating stress-relieving activities such as meditation, yoga, or regular exercise into your daily routine can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being. Moreover, adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while minimizing processed foods and sugary snacks may also contribute to improved skin health.
Key Takeaways:
- Establishing a consistent skincare routine is vital for managing hormonal and fungal acne.
- Use non-comedogenic products that are specifically formulated to not block pores.
- Manage stress levels through activities like meditation, yoga, or exercise.
- Adopt a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while minimizing processed foods and sugary snacks.
Difference Between Hormonal and Fungal Acne
Although hormonal and fungal acne can share some similar symptoms, understanding the differences between them is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Hormonal acne is primarily caused by changes in hormone levels, typically during puberty, menstruation, or times of hormonal imbalance. It often appears as deep red and tender cysts, predominantly in the lower parts of the face such as the chin and jawline. On the other hand, fungal acne is triggered by yeast overgrowth in hair follicles, resulting in small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and spread over larger areas.
To diagnose the type of acne, it is best to consult a dermatologist who can examine the skin and take a detailed medical history. Dermatologists have the expertise to differentiate between hormonal and fungal acne based on the appearance, location, and other associated symptoms. They may also perform additional tests, such as taking a skin sample, to confirm the diagnosis.
Key Differences Between Hormonal and Fungal Acne:
- Hormonal acne is influenced by hormone fluctuations, while fungal acne is caused by yeast overgrowth in hair follicles.
- Hormonal acne appears as deep, tender cysts in the lower parts of the face, whereas fungal acne presents as small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and spread over larger areas.
- Treatment options for hormonal acne often involve topical skincare treatments and hormonal therapies such as birth control pills, while fungal acne typically requires specific antifungal medications, either topical or oral.
In addition to medical intervention, maintaining a consistent skincare routine is essential for managing both hormonal and fungal acne. Using non-comedogenic products that do not clog pores can help prevent further breakouts. Managing stress levels and adopting a healthy diet can also contribute to overall skin health. It is important to note that while these lifestyle modifications can support acne management, they may not be effective as standalone treatments.
Seeking professional help from a dermatologist is recommended for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of hormonal or fungal acne. A dermatologist can provide personalized advice based on an individual's specific condition and help establish an effective treatment plan for long-term acne management.
Lifestyle Modifications for Acne Management
Alongside medical treatments, incorporating simple lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to the management of both hormonal and fungal acne. Adopting a consistent skincare routine is essential for keeping acne-prone skin clean and balanced. Start with a gentle cleanser to remove excess oil and dirt without stripping the skin's natural moisture. Follow up with a non-comedogenic moisturizer that won't clog pores, helping to maintain hydration without exacerbating acne. Regularly exfoliating with a gentle scrub or chemical exfoliant can also help unclog pores and prevent the buildup of dead skin cells.
Skincare Tips to Manage Acne:
- Choose non-comedogenic products: Opt for skincare and cosmetic products labeled non-comedogenic, which means they are formulated to not block pores. This can help reduce the risk of acne flare-ups.
- Avoid harsh and irritating ingredients: Steer clear of products containing alcohol, fragrances, and dyes as they can irritate the skin and worsen acne symptoms.
- Protect your skin: Shield your skin from harmful UV rays by using sunscreen with at least SPF 30, even on cloudy days. Sun exposure can lead to inflammation and worsen acne.
In addition to a proper skincare routine, managing stress levels can also have a positive impact on acne. Stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations, leading to acne breakouts. Engaging in stress management techniques such as regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and getting enough restful sleep can help reduce stress levels and promote clear skin.
Furthermore, diet can play a role in acne management. While the relationship between diet and acne is complex and varies from person to person, some studies suggest that certain foods, such as dairy and high-glycemic index foods, may contribute to acne breakouts in some individuals. Experimenting with your diet and keeping a food diary can help identify any potential triggers. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support overall skin health.
It's important to note that lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient in treating severe or persistent acne. Seeking professional help from a dermatologist is crucial to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Seeking Professional Help
If you are struggling with acne, it is essential to seek professional help from a dermatologist who can accurately diagnose your condition and recommend appropriate treatment options. Acne can be difficult to self-diagnose, as both hormonal acne and fungal acne can have similar symptoms. Visiting a dermatologist will ensure that you receive a proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
A dermatologist will examine your skin and take into account your medical history to determine whether your acne is hormonal or fungal. This is important because the treatment options for hormonal acne and fungal acne differ. Hormonal acne can often be managed with topical skincare treatments and, in some cases, prescribed birth control pills. On the other hand, fungal acne typically requires specific antifungal medications, either topical or oral, to address the underlying yeast overgrowth.
Additionally, a dermatologist can provide valuable guidance on developing a skincare routine that is tailored to your specific needs. They can recommend non-comedogenic products that won't clog your pores and aggravate your acne. They may also discuss lifestyle factors that can contribute to acne, such as stress management and dietary considerations.
Remember, seeking professional help is crucial in effectively managing your acne. A dermatologist has the expertise and knowledge to accurately diagnose your condition and provide targeted treatment options. Don't hesitate to schedule an appointment and take proactive steps towards clearer, healthier skin.

Conclusion
Understanding whether your acne is hormonal or fungal is the first step towards effective treatment, and by consulting a dermatologist, you can receive the guidance necessary to manage and improve your skin condition.
Determining the type of acne can be challenging, as both hormonal and fungal acne can present similar symptoms. Hormonal acne is caused by changes in hormone levels and often appears as deep red and tender cysts, typically in the lower parts of the face. Fungal acne, on the other hand, is caused by yeast overgrowth in hair follicles and manifests as small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and spread over larger areas.
To accurately diagnose the type of acne, it is best to seek professional help from a dermatologist. They can perform a thorough examination of your skin and consider your medical history to make an informed diagnosis. Once the type of acne is identified, appropriate treatment options can be recommended.
Treatment approaches differ for hormonal and fungal acne. Hormonal acne can be managed with topical skincare treatments and may also include the use of birth control pills to regulate hormone levels. Fungal acne, on the other hand, often requires the use of topical or oral antifungal medication to address the underlying yeast overgrowth.
In addition to medical interventions, maintaining a consistent skincare routine and using non-comedogenic products can help manage both hormonal and fungal acne. Managing stress levels and considering dietary factors that may contribute to acne can also be beneficial. By adopting a multi-faceted approach and making lifestyle modifications, you can improve your skin's health and minimize acne breakouts.
Remember, acne is a complex condition that can have various causes. Seeking professional help from a dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. With the right guidance and persistence, you can effectively manage your acne and achieve clearer, healthier skin.
FAQ
Is acne always hormonal?
No, acne can have various causes, including hormonal imbalances, fungal infections, and other factors.
How can I determine if my acne is hormonal or fungal?
It is best to consult a dermatologist who can examine your skin and take a medical history to determine the cause of your acne.
What are the symptoms of hormonal acne?
Hormonal acne often appears as deep red and tender cysts, usually in the lower parts of the face.
What are the symptoms of fungal acne?
Fungal acne typically appears as small, itchy bumps that are uniform in size and spread over larger areas.
How is hormonal acne treated?
Hormonal acne can be treated with topical skincare treatments and birth control pills, which can help balance hormone levels.
How is fungal acne treated?
Fungal acne typically requires topical or oral antifungal medication to target the underlying yeast overgrowth in hair follicles.
What lifestyle factors can help manage acne?
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, using non-comedogenic products, minimizing stress, and considering diet can all contribute to acne management.
What is the difference between hormonal and fungal acne?
Hormonal acne is caused by changes in hormone levels and appears as deep cysts, while fungal acne is caused by yeast overgrowth and appears as small, itchy bumps.
How can I modify my lifestyle to manage acne?
Establishing a skincare routine, using non-comedogenic products, managing stress, and adopting a healthy diet can all help manage acne.
When should I seek professional help for acne?
It is recommended to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment options for your acne.



































































































































